Groceries and supermarkets have made food shopping so easy that we often don’t think about where our food comes from. Meat, vegetables, grains, and other goodies appear magically in our markets, and we reap the benefits.
But something even as simple as rice undergoes a complicated process to get to our grocery stores. The process is pretty interesting, and it might make you rethink the way you look at that next bowl of rice.
It might make your dishes even more satisfying to know so much care and effort has gone into getting the rice to your kitchen. Therefore, it is rather good for you to know how paddy fields work.
How Does Rice Grow in Paddy Fields?
Before planting rice, you must turn over the soil in the paddy to make it soft. This process can be divided into three stages: rough tillage, fine tillage, and leveling.
In the past, you mainly used animal power and plow tools. Animal-like buffaloes are used to prepare the soil for plowing, but now they have been replaced by machines for plowing.

Preparing
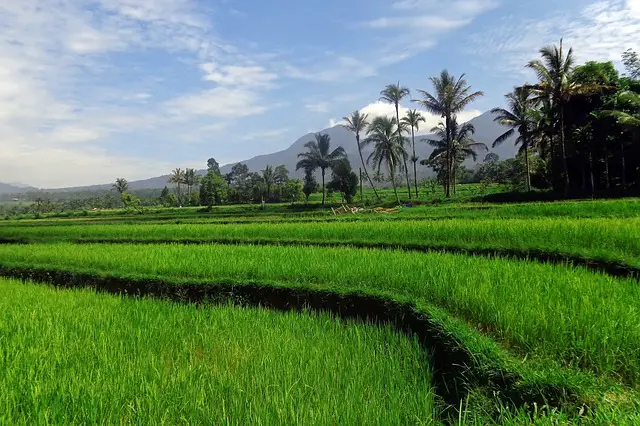
Even before the rice is placed into the ground and grown, there is an elaborate preparation process. Rice needs particular conditions to grow, and fields must be leveled and surrounded by water dikes. The fields are then plowed, and watering equipment is then installed into the rice fields.
Planting
After the seeds are washed, they are either planted into the ground by hand or by airplane. In most Asian countries, rice is still planted by hand because most farmers are poor.
Laborers will painstakingly plant each seed by hand, making sure to leave enough space between seeds. After about a month, these seeds are moved from nursery beds to paddy fields. In the States, rice seeds are usually planted by a low-flying airplane.
Harvesting
Ever wonder how long does it take to harvest rice? Well, generally, after three months of growth, rice is ready to be harvested and picked. The water is drained from the paddy fields, which causes the rice grains to ripen further. In Asian countries, these seeds are harvested by hand, while in the States, there is usually elaborate equipment that can harvest the seeds mechanically.
The grains are then put into racks placed under the sun or a mechanical heater. This takes away more moisture from the grains and allows the rice to ripen further.
Hulling and Milling
The rice grains then go through a process that removes the outer hulls from the inner grains. Hulling is basically a rough process that bangs and smashes the hulls from the centers. Some farmers do this by hand using stones, while others rely on equipment to perform this task.
Once the hulls are removed, they are thrown away, and the rice grains are left behind. In some cases, a thin layer of glucose is added to the grains to add sheen and color.
Enriching Process
Because most of the nutrients in rice lie in the hulls, the enriching process has to be done to add the vitamins and minerals back into it. The pressure is often used to transfer the nutrients from the hulls into the kernels. In some cases, rice is placed into a nutrient-rich bath that further infuses the kernels with vitamins and minerals.

Packaging
The rice is then left to dry and placed into large satchels or bags sent to our local markets and grocery stores. Pricing depends largely on the region where the rice has come from and the types of kernels that have been harvested.
As you can see, there’s a lot that goes on to get this seemingly simple grain onto your plate. It takes a lot of time and workforce to access these delicious grains.
Your Dinner Table
The price you’ve purchased at the supermarket has gone through an incredible journey. But now it’s going to its most exciting adventure yet. It’s about to be turned into a delicious dish for your family to enjoy.
Rice is a great food to work with because it offers a lot of versatility while absorbing all of your favorite flavors. You can use it as a side for scrumptious meals. This features prime rib or baked salmon.
You can also feature it more prominently with a hearty dish is like risotto. It also provides wonderful opportunities to explore other cultures and their cuisine, especially Asian ones. How about homemade sushi for your next family meal? Would congee hit the spot? It’s all made possible with rice.
What is the Difference Between Rice and Paddy?
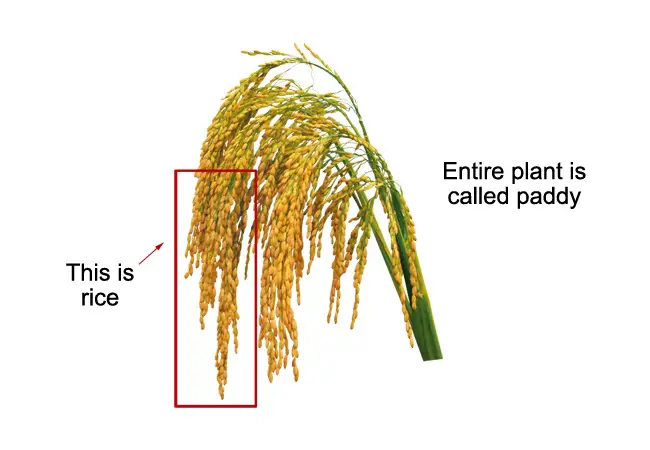
Have you ever been curious about the difference between rice and paddy? The difference between rice and paddy is the field that grows the paddy is called the paddy field. The entire plant that grows from the paddy field is called paddy. The crop that can be harvested and eaten is called rice.
In Chinese, paddy before cooking is called mi (米), and after cooked is called fun(饭). But in English, it is called rice doesn’t matter whether it is before or after cooking.
We can begin by examining how they differ from one another. Rice is a grain crop that, depending on how it’s processed after harvesting, comes in a wide range of colors, from white to brown to red. Thiamine (vitamin B1), iron, and calcium are just some of the essential vitamins and minerals it provides.
Paddy, also known as rough rice or hulled rice, refers to unprocessed grains with an outer husk layer attached to them. Unlike polished white rice that goes through milling processes where husks and bran layers are removed; paddy still retains all-natural nutrients within it including dietary fiber that helps regulate digestion while providing energy for us during physical activities.
There are different ways to use each product – both domestically and commercially. The most common way of consuming cooked rice is by boiling it in water until it softens up enough to eat; whereas paddy may either be used directly for culinary purposes or further milled down into other products like flour for baking goods or snacks like crackers etc., making them more versatile than just being boiled for consumption alone.
Paddy can also be used as fodder for livestock due to its rich nutritional content; something which cannot be done with fully-milled white/brown rice since all valuable nutrition would have been stripped away from it along with its husks during processing stages prior to packaging & selling at stores worldwide.
Therefore, although both products share similar origins when discussing their differences one must consider factors such as potential utility value & available nutrient composition before deciding which option suits best according to individual preference & situation at hand – whether it’s preparing meals at home or serving customers in commercial settings alike!
How to Increase Paddy Yield?
Early morning sunlight cascades through the clouds stretching its golden rays across the vast expanse of lush green paddy fields. The faint smell of soil and rich nutrients fills the air with a sense of possibility as farmers eagerly prepare for another harvest season.
It is no secret that increasing yields in crop production has been a longstanding challenge faced by agriculturalists around the globe, but it doesn’t have to be an insurmountable obstacle. With proper knowledge and implementation of appropriate techniques, crops such as rice can yield higher-quality products while also reducing input costs.
In order to improve paddy yield, agronomists suggest implementing integrated nutrient management (INM) practices which include planting on-farm compost or manure, rotating different types of crops, enriching soil fertility levels with organic matter such as cowpea residues and fish waste; applying balanced fertilizer doses based on soil test results; using efficient irrigation methods like drip irrigation or sprinkler systems; controlling weeds manually or chemically; maintaining healthy seedbeds; and taking timely steps against diseases and pests. Additionally, genetic modification may also prove useful in yielding better harvests from existing land resources if utilized ethically.
By focusing on sustainable farming practices like INM along with advancements in biotechnology, high-yielding varieties can be developed that are resilient to changing climatic conditions yet still maintain their nutritional value. This will not only help increase yields but also benefit both smallholder and commercial farmers alike who depend heavily on successful crop production for their livelihoods.
How do Paddy Fields Produce Methane?
The amount of methane released is affected by the photosynthesis of paddy plants. Paddy growth produces methane gas by feeding microbes living under the paddy fields.
Rice farming is one of the main causes that generated methane gas. In a world that is affected by climate change, growing rice is becoming less environmentally friendly.
Higher levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere cause rice in paddy fields to grow faster. This, in turn, accelerates the microbes living under the rice fields and causes more methane to enter the atmosphere.
In addition, rising temperatures will reduce rice production, which means that more methane is produced in the paddy field. However, if the farmers adopt new farming techniques, they can actually solve this problem.
For example, since 2000, Chinese rice farmers have begun to drain rice fields instead of flooding rice fields in the middle of the growing season and using different fertilizers, which have greatly reduced methane emissions.
Other recommendations from scientists include switching to heat-tolerant rice and changing the dates for planting and harvesting. This will help alleviate the problem of reduced production and effectively reduce methane emissions of paddy fields.
Read also: Innovative New Farming Methods To Boost Production